The Complete Guide to Berries: Nature's Superfood for Health and Wellness
Berries are nature's powerhouse, brimming with nutritional benefits and a rich history of medicinal use. Their unique anatomy—comprising the outer exocarp, the fleshy mesocarp, and the protective endocarp surrounding multiple seeds—sets them apart from other fruits. But there's so much more to these vibrant gems than meets the eye.
Unmatched Nutritional Value
Berries are celebrated for their abundance of essential vitamins, minerals, and potent antioxidants. They are one of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet, making them a staple in any diet aimed at achieving optimal health. Antioxidants like anthocyanins, flavonoids, and polyphenols found in berries help combat oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, and promote overall well-being. Whether you're looking to boost your immune system, enhance heart health, or improve digestion, berries offer a natural, effective solution.
Berries in Traditional Medicine
For centuries, berries have been integral to traditional medicine across various cultures. Herbalists have long recognized their anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and detoxifying properties. For example:
- Hawthorn berries are renowned for supporting cardiovascular health and regulating blood pressure.
- Goji berries, often dubbed a superfood, are prized for their ability to boost immunity, improve skin health, and enhance energy levels.
- Juniper berries have been used for their detoxifying properties, particularly in supporting kidney and urinary health.
These medicinal uses are backed by modern scientific research, making berries not only a nutritional powerhouse but also a valuable tool in natural healing practices.
The Role of Berries in Skincare
Beyond their internal health benefits, berries are also highly regarded in the skincare industry. Their high levels of vitamin C and antioxidants help rejuvenate the skin, reduce signs of aging, and provide a radiant complexion. Whether in the form of oils, creams, or masks, berries like blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are commonly found in skincare products designed to nourish and protect the skin.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Berries have played a significant role in the culinary and medicinal traditions of many cultures. From ancient herbalists to modern nutritionists, the value of berries has transcended time. Their use in everything from teas to tinctures to skincare illustrates their versatility and enduring relevance in the pursuit of health and wellness.
Why Berries Should Be a Staple in Your Diet
With their impressive nutritional profile and countless health benefits, incorporating berries into your daily routine is one of the easiest ways to improve your health. Whether consumed fresh, dried, or as part of supplements and skincare, these fruits offer a wealth of advantages that few other foods can match.
Boost your well-being today by making berries a staple in your diet. Experience the full spectrum of benefits they provide, from enhancing your immune system to protecting your skin—nature’s superfood has never been more powerful.

Berries are small, fleshy fruits that develop from a single flower's ovary and contain multiple seeds, encased in a soft, often colorful outer skin. Their flavors range from sweet to tart, making them a diverse and popular fruit. Common examples include strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, hawthorn berries, goji berries, lycium berries, and schisandra berries. Interestingly, fruits like grapes, tomatoes, cucumbers (classified as epigynous or false berries from an inferior ovary), and eggplants also belong to the berry family. Berries with thick or tough rinds are known as Pepo, such as watermelons, pumpkins, and cantaloupes.
Parts of Berries
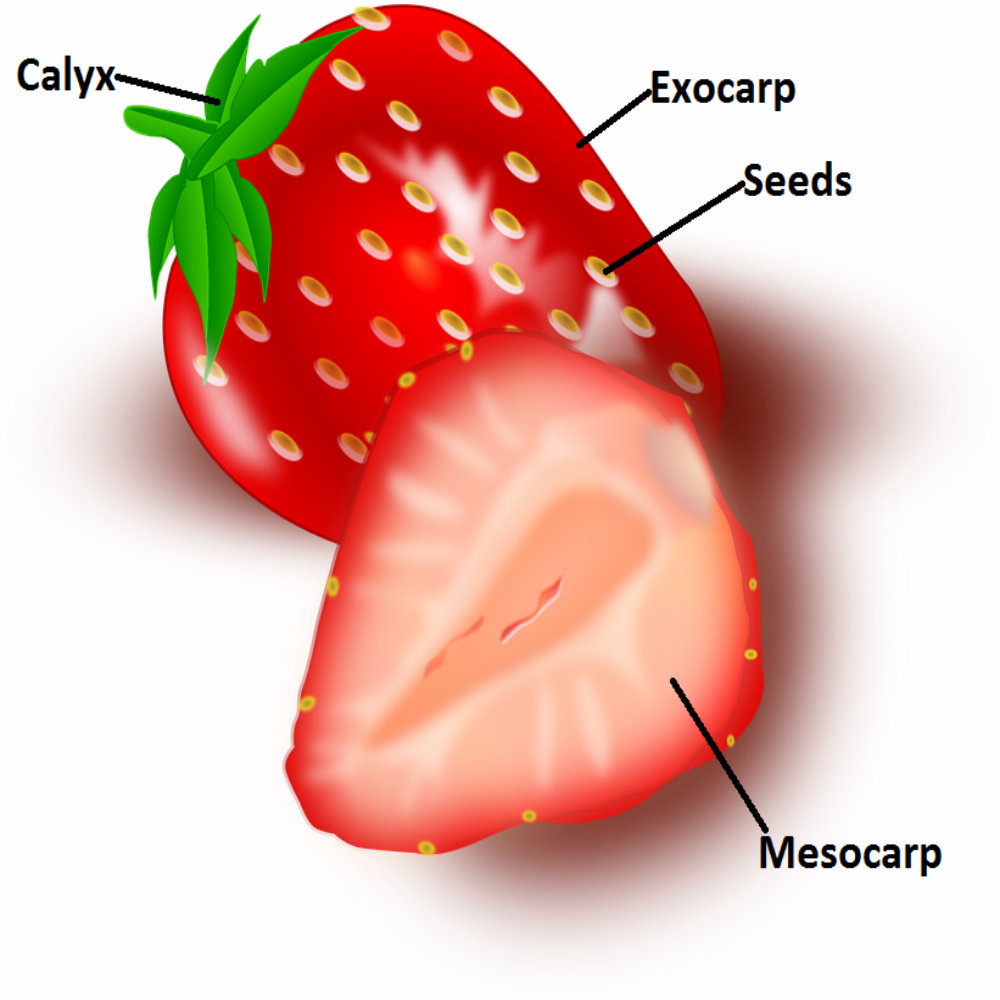
Calyx – The outer part of the flower formed by the sepals (the outer leaves of a bud)
Exocarp – The outer protective skin. In true berries the skin is soft.
Seeds – Are located in the flesh of the berry. In most berries the seed are located in mesocarp, but in strawberries they are in the exocarp.
Mesocarp – The inner flesh (pulp) of the berry
The terms "fruit" and "berry" are often used interchangeably in everyday language, but botanically, there are distinctions between them:
Fruit: In botanical terms, a fruit is the mature ovary of a flowering plant, typically containing seeds. It develops from the fertilized ovary after pollination and serves as a means of seed dispersal. Fruits can be classified into various types based on their structure, such as fleshy fruits (like apples and oranges) and dry fruits (like nuts and beans).
Berry: A berry is a specific type of fleshy fruit that develops from a single ovary and typically contains multiple seeds embedded in the flesh. Botanically, berries have three distinct layers: the exocarp (outer skin), the mesocarp (fleshy middle layer), and the endocarp (innermost layer surrounding the seeds). Berries can come from various plant families and exhibit a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors.
So, while all berries are fruits, not all fruits are berries. Berries have a specific botanical definition that distinguishes them from other types of fruits based on their structure and development. Examples of true berries include tomatoes, grapes, and bananas.
© 1stChineseHerbs.com
References
http://waynesword.palomar.edu/termfr4.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berry
https://pixabay.com
Images used were found with a search for images with a “free to use and share” license on 4-4-2016.
http://www.answers.com/Q/Is_a_cucumber_a_berry

