Dang Shen “Gentle Ginseng” Guide: How It Works, Best Uses, Dosing, and What to Buy
Dang Shen (Codonopsis pilosula) is one of the most trusted “daily builder” herbs in Traditional Chinese Medicine—yet most pages leave shoppers with the same questions: How do I actually use it? Is it like ginseng? Why is there dextrin in extract powder? How long does it take to notice anything? And who should avoid it?
This guide answers those questions clearly and responsibly. You’ll learn what Dang Shen is traditionally used for, how concentrated extract powders work, the easiest ways to use it in soups, broths, and simple blends, what “Spleen and Lung support” means in plain English, and what to watch for in safety and quality—so you can choose the right form and use it consistently.
Quick Summary Box
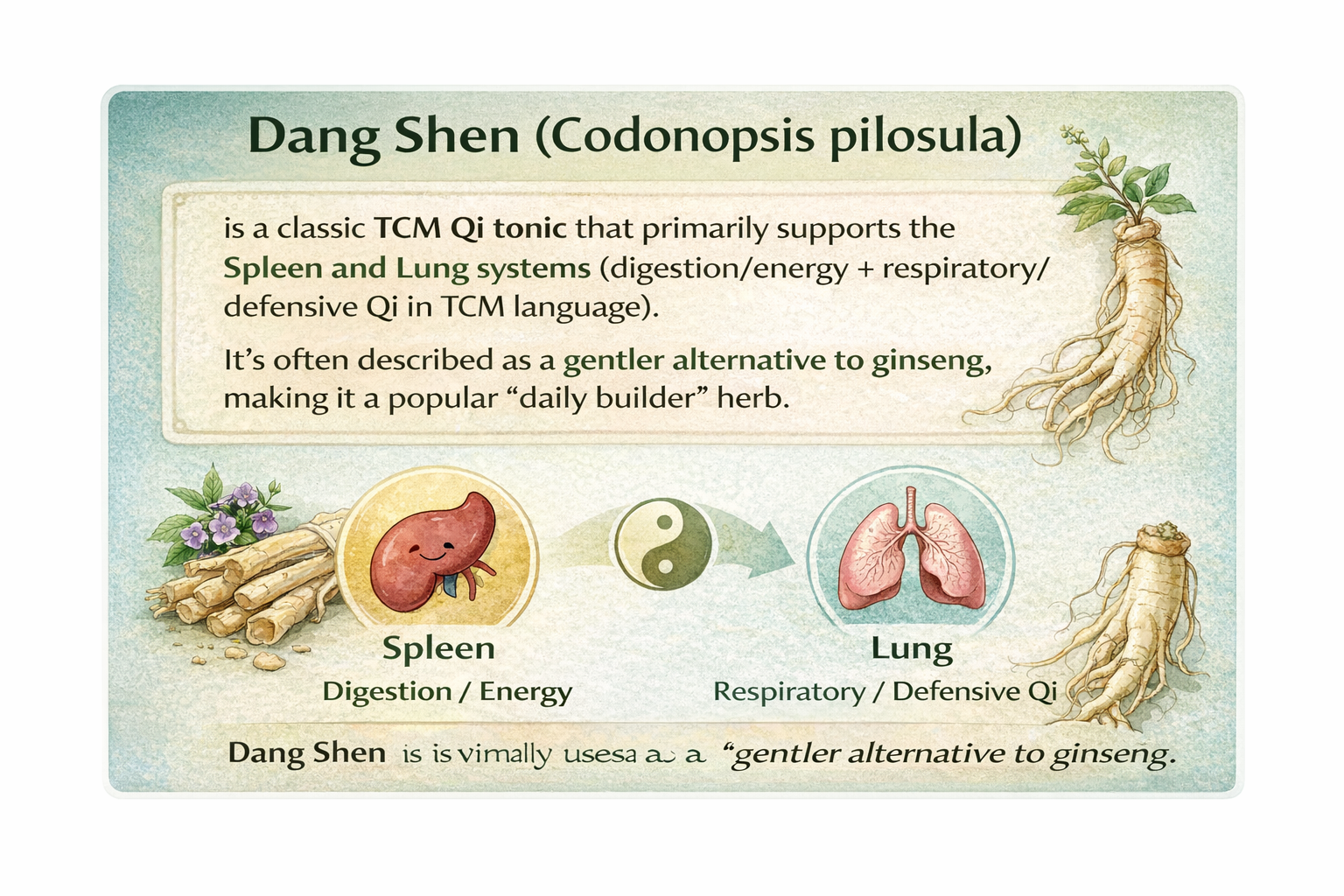
Dang Shen (Codonopsis root) is a classic TCM Qi tonic traditionally used to support the Spleen and Lung systems—which often translates to digestion/energy + respiratory/defensive
Dang Shen Quick Facts
-
Common Name: Codonopsis Root, Codonopsis pilosula root
-
Botanical Name: Codonopsis pilosula (Radix)
-
Pin Yin: Dang Shen
-
TCM Nature/Flavor: Sweet, Neutral
-
Meridians/Channels: Lung, Spleen
-
Form: Full Spectrum Extract Powder (concentrated)
-
Other Ingredients: Dextrin (derived from non-GMO corn)
-
Package Size: 100 g
-
Origin: China
-
Brand: Plum Flower (species-authenticated)
-
Cautions (store policy): Avoid if pregnant/nursing; avoid during digestive infection (per your existing guidance).
-
Prop 65: Add your standard Prop 65 statement (California customers)
This information is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Statements about herbs have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Consult a qualified healthcare professional before use if you are pregnant, nursing, have a medical condition, take medications, or are preparing for surgery.
PubMed / Research Links
Mechanisms and potential pharmacological effects of Codonopsis pilosula (review, PMC): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11128667/
Immune Support / Immune Regulation (PubMed)
-
Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides: structure + immune regulatory activity (review)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41058688/ -
Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides, intestinal flora, and intestinal homeostasis (review)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41500286/ -
Radix Codonopsis polysaccharide: immune balance / immunomodulatory activity
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30797152/ -
Codonopsis polysaccharide: structure characterization + immunomodulatory effects in THP-1 cell model
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39450708/
Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant Activity
-
Pectic polysaccharide from Codonopsis pilosula: reduced inflammatory response + oxidative stress (mouse model)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37760084/ -
Full text (PubMed Central) version of the same study
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10525188/
Gut Microbiome / Gut–Immune Axis (PubMed)
-
Codonopsis polysaccharides and gut microbiota dysbiosis (preclinical)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38897503/ -
Alkali-extracted Codonopsis polysaccharide: gut microbiota effects (preclinical)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40871255/