The Nutritional Power of Peels and Rinds: Health Benefits You Never Knew
We all love citrus fruits—whether it's snacking on a sweet orange or adding a refreshing squirt of lemon to our favorite dish. Citrus fruits are known for their wealth of vitamins, minerals, and fiber that not only please our taste buds but also boost our health. But have you ever thought about the benefits of the peel? Citrus peels, often overlooked, are nutritional powerhouses in their own right. There’s so much more to a peel than just zesting!
Why Citrus Peels Matter for Your Health
Modern research has confirmed what herbalists have known for centuries: citrus peels are packed with insoluble fiber, which is essential for a healthy digestive system. But that’s just the beginning. These peels are also rich in antioxidants, vitamin C, and flavonoids that support overall well-being. The Chinese, for example, have used the rinds of mandarin oranges and bitter oranges for centuries to support digestive health and improve respiratory function.
Benefits of Citrus Peels Beyond Zest
Citrus peels aren’t just a source of flavor—they’re a functional, health-boosting ingredient. By incorporating citrus peels into your diet, you gain access to:
- Digestive support through high fiber content
- Enhanced respiratory health with potent bioactive compounds
- Antioxidant protection that helps fight oxidative stress
- Blood sugar regulation due to naturally occurring compounds that help balance insulin
Herbalists across time have tapped into these benefits, and now modern science is catching up. Whether dried, powdered, or fresh, citrus peels offer a natural, powerful addition to both your diet and your wellness routine.
Start incorporating these often-overlooked peels into your life today, and unlock the hidden nutritional benefits they provide.
Bulk herbs in peel form:
Parts of a Citrus Peel/Rind
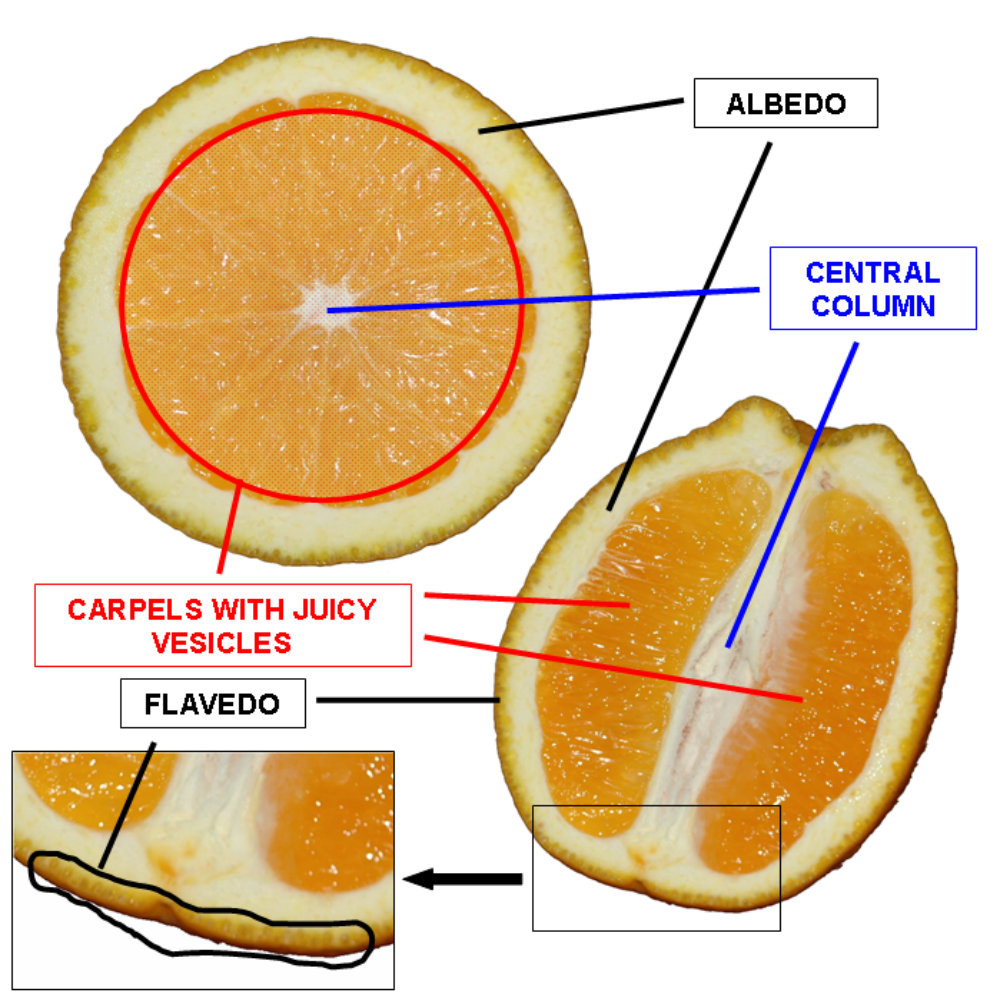
Flavedo – The tough outer skin of the fruit. It contains cellulose, essential oils, paraffin waxes, steroids, triterpenoids, fatty acids, pigments, limonene which are bitter, and enzymes.
Albedo – In inner part of the rind (peel). It is also referred to as the pith.
Carpels with Juicy Vesicles – The pulp of the fruit that is usually eaten.
Central Column – Is the core of the fruit.

© 1stChineseHerbs.com
References
http://www.motherearthliving.com/health-and-wellness/citrus-peel-medicine.aspx
https://pixabay.com/en/orange-citrus-fruit-fruit-healthy-644093/ CC0 Public Domain Free for commercial use
No attribution required April 4th 2016
http://foodingredients.wikispaces.com/Elizabeth-Gums+and+stabilizers

