The Essential Role of Roots in Natural Medicine and Plant Survival
Roots have been integral to natural medicine for centuries, forming the basis of many herbal remedies and even contributing to modern pharmaceuticals. From their role in anchoring plants to their vital function in nutrient absorption, roots are a cornerstone of both botanical science and traditional healing practices. Some of the most well-known roots used in natural medicine include Abscess root, Henna root, and Licorice root. Even today, roots continue to be sources of potent medicinal compounds, such as inulin, which was first derived from dahlia roots and is now a popular supplement for gut health and blood sugar regulation.
The Anatomy and Function of Roots
Roots serve as the foundation of a plant, both figuratively and literally. They are typically found underground, where they anchor the plant and absorb water, minerals, and other nutrients from the soil, transporting these vital substances to the rest of the plant. But their role goes far beyond basic support:
- Anchoring: Roots secure the plant in the soil, providing stability, particularly in windy or unstable conditions. Without a strong root system, plants would struggle to survive in many environments.
- Nutrient Absorption: Roots have a specialized structure known as root hairs, which increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. This ensures that plants receive the essential minerals they need to grow and thrive.
- Water Transport: Through the process of osmosis, roots pull water from the soil into the plant, helping to maintain turgor pressure, which keeps the plant upright and hydrated.
Types of Roots in Natural Medicine
Many roots have long been revered for their medicinal properties, and their uses span centuries and cultures. Here are a few notable examples:
- Abscess Root: Known for its use in treating abscesses, inflammation, and other skin conditions, abscess root has strong anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
- Henna Root: Beyond its cosmetic uses in hair and skin coloring, henna root has been used in traditional medicine for its cooling and antibacterial effects, making it useful in treating burns, wounds, and infections.
- Licorice Root: One of the most famous medicinal roots, licorice root is prized for its anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and immune-boosting properties. It has been used to soothe sore throats, support digestion, and alleviate respiratory conditions.
The Evolution of Modern Medicine from Roots
Many of today's pharmaceutical advancements have their origins in plant roots. For example, inulin, a type of soluble fiber that helps regulate blood sugar and supports digestive health, was first discovered in the roots of the dahlia plant. Inulin is now widely used as a prebiotic supplement, demonstrating how ancient remedies have evolved into modern health solutions.
- Medicinal Alkaloids: Some roots, like those from the Mandrake and Echinacea plants, contain alkaloids that are still used today in pain relief and immune support. These naturally occurring compounds show the ongoing relevance of roots in medicinal science.
Roots as Nutrient Reservoirs
Roots are not just channels for nutrient absorption; they also act as storage units for the plant. Many plants store carbohydrates, starch, and other essential nutrients in their roots to survive harsh seasons like winter or drought. This stored energy is crucial for the plant's regrowth when conditions improve. This is particularly true for plants like carrots, beets, and sweet potatoes, which store large amounts of energy in their roots and are commonly consumed for their nutritional benefits.
Roots in Culinary Use
While many roots are recognized for their medicinal properties, they also play a vital role in culinary traditions around the world. Edible roots like ginger, turmeric, and garlic not only enhance the flavor of dishes but also offer numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Ginger Root: Widely used in Asian cuisine, ginger is not only a flavor enhancer but also helps with digestion, nausea, and inflammation.
- Turmeric Root: Known for its bright yellow color and curcumin content, turmeric is a staple in both food and medicine, particularly in traditional Indian Ayurvedic practices.
The Ecological Importance of Roots
Roots play a critical role in soil health and ecosystem stability. By anchoring plants, they prevent soil erosion, and their intricate network of root systems helps to create and maintain healthy soil structure. Roots also participate in a symbiotic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi, which enhances nutrient uptake and supports the broader ecosystem.
In ecosystems that face frequent disturbances, such as fires or floods, roots help plants regenerate by storing nutrients that can be tapped into when above-ground parts of the plant are damaged or destroyed.
Vegetative Reproduction through Roots
Certain plants are capable of vegetative reproduction through their roots, meaning they can produce new plants without seeds. This is particularly common in plants like sweet potatoes, dandelions, and asparagus, which use their root systems to generate new growth. This ability allows plants to colonize new areas, survive adverse conditions, and thrive over multiple growing seasons.
Conclusion: Roots as the Foundation of Medicine and Plant Life
Roots are far more than just the underground part of a plant. They are a complex, multifunctional system essential to the survival and thriving of plants, as well as a rich source of medicinal compounds that have been used for centuries. From ancient herbal remedies to modern medicine, roots continue to be at the forefront of natural healing and human health.
As we continue to discover more about the benefits of roots, their importance in both the ecological world and natural medicine becomes even more apparent. Whether you're seeking botanical remedies, nutrient-rich foods, or an understanding of how plants thrive, roots are a foundational element that cannot be overlooked.
Parts of a Root
Roots have a variety of different parts. See the diagram on the left to identify what each part of the root is.
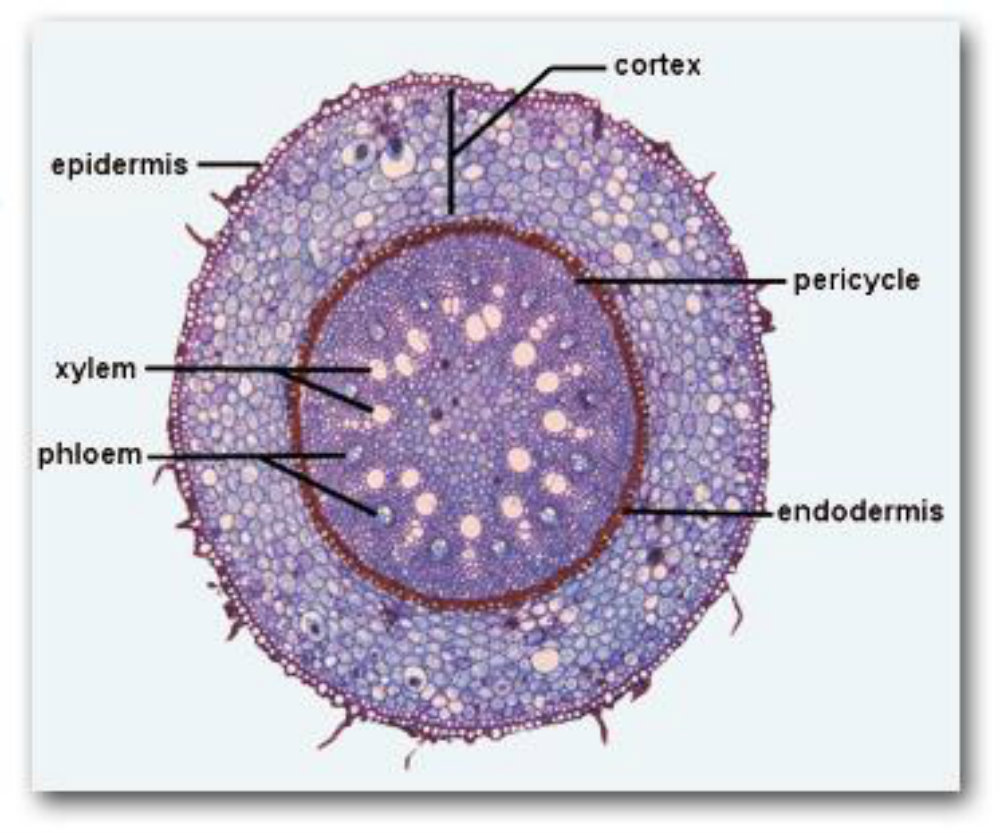 Epidermis: Is the outer surface of the root. It protects the inner structures.
Epidermis: Is the outer surface of the root. It protects the inner structures.
Cortex: Makes up most of the root.
Endodermis: A layer of tightly packed cells on the innermost surface of the cortex.
Pericycle: The outer wall of the Vascular Cylinder (center of the root). It contains several layers, This is where the lateral roots grow from.
Xylem: Part of the Vascular Cylinder. It is vascular tissue in the root that transports water and nutrients upward in the root. Makes the woody part of the root,
Phloem: Part of the Vascular Cylinder. It is a vascular tissue that transports food made by photosynthesis to all parts of the plant.


© 1stChineseHerbs.com
References
https://ag.arizona.edu/pubs/garden/mg/botany/roots.html
http://www.naturecures.co.uk/rootvegetables.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_plants_used_in_herbalism
Image reference: http://ap-bio-chs-plants.wikispaces.com/Primary+Structure+of+Roots+and+Stems
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dicotyledoneae_Asteraceae_herb_-_root_system,_primary_root_becomes_tap_root_and_lateral_roots.JPG
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:2011-03-22_Poa-annua-roots.JPG
This image was found in a search for an image licensed for reuse on 3-28-2016

