The Ultimate Guide to Cholesterol: Your Path to a Healthier Heart and Liver
Sep 4th 2024
The Ultimate Guide to Cholesterol: Your Path to a Healthier Heart and Liver
Cholesterol often gets a bad rap, but it plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of our bodies. Whether you're looking to understand the difference between good and bad cholesterol or seeking natural ways to keep your levels in check, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know. Let's dive into how cholesterol affects your heart, liver, and overall well-being, and what you can do to manage it effectively.
What is Cholesterol, and Why Do You Need It?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that exists in every cell of your body. It's essential for producing vital hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, which regulate many of your body’s processes. It also aids in the production of vitamin D, important for bone health and immune function, and is key for making bile acids that help digest dietary fats.
However, problems arise when cholesterol levels get too high. Too much cholesterol, especially low-density lipoprotein (LDL), can lead to a buildup of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart disease, strokes, and other serious health issues.

LDL Cholesterol: The "Bad" Kind
LDL, often labeled as "bad cholesterol," is harmful because it transports cholesterol to your arteries. When there’s too much LDL, it sticks to artery walls, creating plaques that narrow and harden your arteries—a condition known as atherosclerosis.
Why High LDL Levels Are Dangerous
When LDL levels are high, the risk of:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease ... skyrockets. The narrowed arteries can't supply enough oxygen-rich blood to your organs, including the heart and brain, leading to life-threatening conditions.
Key factors that raise LDL:
- Diets high in saturated fats and trans fats
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Genetics (such as familial hypercholesterolemia)
How to manage LDL:
- Eat more fiber-rich foods (whole grains, fruits, vegetables)
- Exercise regularly
- Quit smoking
- Consider cholesterol-lowering medications, like statins, if prescribed by your healthcare provider.
HDL Cholesterol: The "Good" Kind
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is your friend. It helps remove excess cholesterol from your bloodstream and transports it back to the liver, where it's processed and eliminated from the body. Having higher levels of HDL can help protect you from heart disease and stroke.
How to boost HDL:
- Engage in regular aerobic exercise
- Eat healthy fats, like those found in fish, nuts, and seeds
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid smoking
- If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation
Triglycerides: The Forgotten Fat
While most people focus on cholesterol, triglycerides are another type of fat that you should be mindful of. Triglycerides store excess calories and are used for energy, but high levels can increase your risk for heart disease, particularly when paired with low HDL or high LDL.
Elevated triglyceride levels may indicate:
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Fatty liver disease
How to lower triglycerides:
- Reduce sugar and refined carbohydrates in your diet
- Increase fiber and omega-3 fatty acids
- Get regular exercise
- Aim for a healthy weight
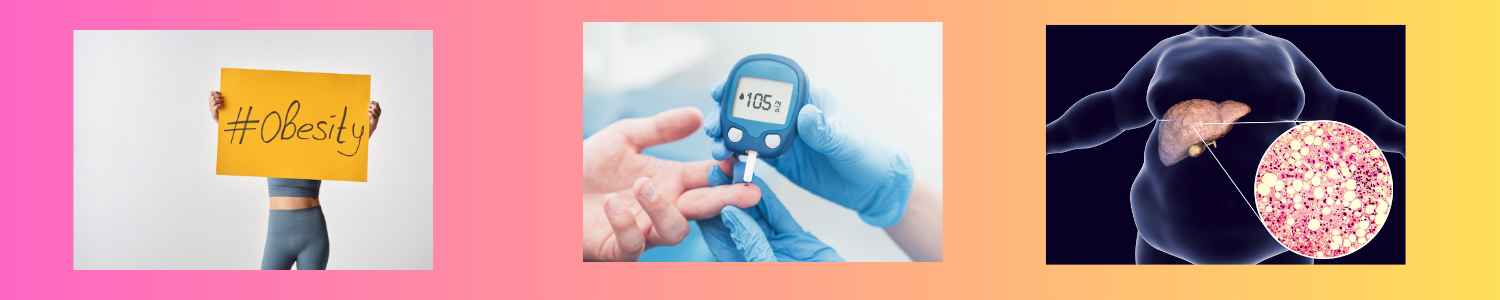
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Cholesterol
High cholesterol doesn’t just affect your heart—it can also impact your liver. NAFLD occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver, often in people with high LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. Left untreated, it can progress to cirrhosis or liver failure.
Cholesterol and Heart Disease: Why It Matters
High cholesterol, especially LDL, contributes to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaques form in your arteries. This restricts blood flow and can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology showed that lowering LDL through lifestyle changes and medications significantly reduces the risk of coronary artery disease.

Herbal Remedies for Cholesterol Reduction: Nature’s Best Medicine
If you're looking to manage cholesterol naturally, consider these herbal remedies:
- Guggul (Commiphora mukul): This Ayurvedic staple has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.): A key herb in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for heart health, Hawthorn lowers cholesterol and improves circulation.
- Artichoke Leaf (Cynara scolymus): Research shows that it inhibits cholesterol production in the liver.
- Garlic (Allium sativum): Garlic is known to lower total cholesterol, particularly LDL, and boost HDL.
- Dan Shen (Salvia miltiorrhiza): A TCM herb that improves circulation and reduces LDL cholesterol levels.
- Astragalus Root (Astragalus membranaceus): Astragalus supports heart health by lowering LDL and reducing plaque buildup.
Foods to Eat for Lower Cholesterol: Building a Heart-Healthy Diet
What you eat plays a major role in managing cholesterol. Here are some cholesterol-lowering foods to include in your diet:
- Oats and Barley: Rich in soluble fiber, they help lower LDL.
- Fatty Fish: Loaded with omega-3s, which lower triglycerides and raise HDL.
- Nuts: Full of unsaturated fats and fiber, nuts reduce LDL.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas help lower cholesterol.
Daily meal plan ideas:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal topped with berries and almonds.
- Lunch: A mixed green salad with chickpeas, avocado, and olive oil.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with steamed broccoli and quinoa.
Foods to Avoid: Cholesterol Traps
Certain foods can raise cholesterol levels, especially those high in saturated fats and trans fats. Avoid:
- Red Meat
- Butter and Full-Fat Dairy
- Fried Foods
- Pastries and Baked Goods
Processed foods and refined carbs can also raise triglycerides and lower HDL, making them equally dangerous for cholesterol levels.
The Importance of Reducing Cholesterol for Heart and Liver Health
By reducing your cholesterol, you don’t just protect your heart—you also reduce your risk of NAFLD, liver damage, and cirrhosis. Managing your cholesterol today can save you from heart attacks, strokes, and long-term liver issues.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower Cholesterol
Small, consistent lifestyle changes can make a big impact on your cholesterol levels:
- Exercise regularly to raise HDL and lower LDL.
- Reduce stress through mindfulness, yoga, or meditation.
- Quit smoking to improve HDL levels.
- Limit alcohol to avoid raising triglycerides.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Cholesterol
Managing cholesterol isn’t just about numbers—it’s about taking control of your health for a longer, happier life. Whether through diet, exercise, herbal remedies, or medications, every step you take matters. By following these strategies, you can improve your cholesterol levels, protect your heart, and prevent serious liver diseases.
Remember, even small adjustments can have a big impact on your health over time!
Disclaimer: Always consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet, exercise, or health regimen. This guide is intended for educational purposes and does not substitute for professional medical advice.


